Inheritance vs. Composition in Java
This article illustrates the concepts of inheritance vs. composition in Java. It first shows an example of inheritance, and then shows how to improve the inheritance design by using composition. How to choose between them is summarized at the end.
1. Inheritance
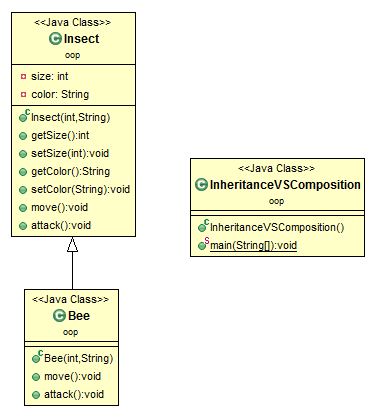
Let's suppose we have an
Insect class. This class contains two methods: 1) move() and 2)attack().
Now you want to define a
Bee class, which is a type of Insect, but have different implementations ofattack() and move(). This can be done by using an inheritance design like the following:
The class hierarchy diagram is as simple as:
Output:
Fly Fly Attack
"Fly" was printed twice, which indicates
move() is called twice. But it should be called only ONCE.
The problem is caused by the
super.attack() method. The attack() method of Insect invokesmove() method. When the subclass calls super.attack(), it also invokes the overridden move()method.
To fix the problem, we can:
- eliminate the subclass's
attack()method. This will make the subclass depends on the superclass's implementation ofattack(). If theattack()method in the superclass is changed later (which is out of your control), e.g., the superclass'sattack()method use another method to move, the subclass will need to be changed too. This is bad encapsulation. - rewrite the
attack()method like the following:This would guarantee the correct result, because the subclass is not dependent on the superclass any more. However, the code is the duplicate of the superclass. (Imageattack()method does complex things other than just printing a string) This does not following software engineering rule of reusing.
This inheritance design is bad, because the subclass depends on the implementation details of its superclass. If the superclass changes, the subclass may break.
2. Composition
Instead of inheritance, composition can be used in this case. Let's first take a look at the composition solution.
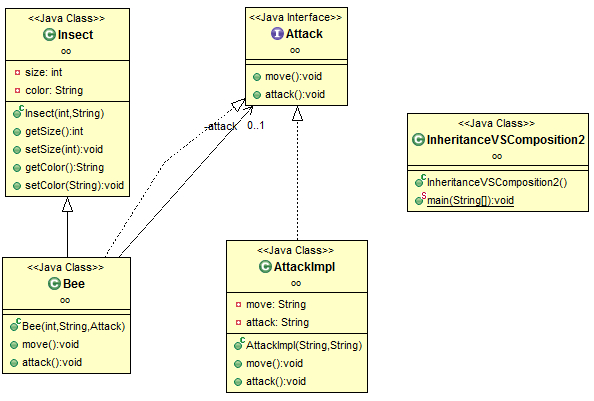
The attack function is abstracted as an interface.
Different kinds of attack can be defined by implementing the
Attack interface.
Since the attack function is extracted,
Insect does not do anything related with attack any longer.
Bee is a type of
Insect, it can attack.
Class Diagram:

fly move fly sting
3. When to Use Which?
The following two items can guide the selection between inheritance and composition:
- If there is an IS-A relation, and a class wants to expose all the interface to another class, inheritance is likely to be preferred.
- If there is a HAS-A relationship, composition is preferred.
In summary, Inheritance and composition both have their uses, and it pays to understand their relative merits.
No comments:
Post a Comment